Hexagonal perforation
High open area, strength, low weight and aesthetic appeal

Hexagonal perforation provides a high open area while maintaining material strength. The honeycomb structure of hexagonal holes allows for optimal airflow and efficient material use, making it a common choice for effective ventilation, cooling, and filtration applications.
Key benefits of hexagonal perforation
- Provides maximum open area for ventilation, filtration, and material throughput.
- Available with open areas of up to 85% for high-efficiency airflow.
- Lightweight yet strong, ensuring durability while optimising material usage.
- Suitable for both functional and aesthetic applications, offering modern and clean designs.
Applications examples
-
Ventilation and cooling: Ideal for server cabinets, electronic enclosures, and industrial machinery, allowing for effective heat dissipation and airflow control.
-
Filtration and separation: Used in food processing, chemical industries, and bulk material handling, providing efficient material flow while maintaining strength.
-
Industrial screening: Used in sieves and screening systems for agriculture, recycling, and material sorting, ensuring high throughput.
-
Architectural applications: Applied in facades, balustrades, and sunscreens, combining functionality with an appealing and distinctive pattern.
Technical information - hexagonal perforation
Arrangement of holes
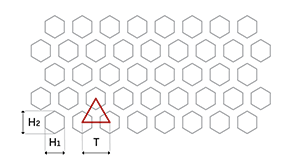
Hexagonal holes (H) with a 60° staggered triangular pitch (T) are the most widely used arrangement for hexagonal perforation, offering high mechanical strength and optimal open areas. The equal spacing between holes of this arrangement maintains uniform strength, even with a reduced pitch.
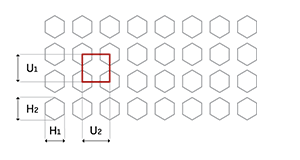
Hexagonal holes (H) with a rectangular pitch (U) align in straight, uniform rows, creating a grid-like pattern with predictable strength and open areas. This layout suits applications needing controlled airflow or a structured, decorative appearance.
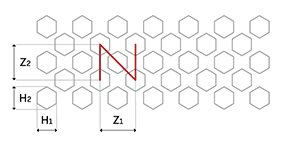
Hexagonal holes (H) with a staggered pitch (Z) provide balanced open areas and structural stability. Ideal for applications requiring airflow and durability, the Z configuration combines flexibility and strength.
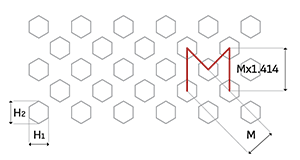
Hexagonal holes (H) with a diagonal pitch (M), also known as 45° staggered pitch, offer unique design options and moderate open areas. This alignment adds visual appeal without sacrificing strength, perfect for aesthetics-focused applications.
T = Triangular pitch
U = Rectangular pitch
Z = Staggered pitch
M = Diagonal pitch
Beginning and end of perforated areas
A closed end pattern involves special tooling to create a uniform edge at the start and end of the perforated area, giving a clean, continuous look ideal for decorative and architectural applications. This process is more costly and may extend production time.
A semi-closed end pattern balances cost-effectiveness and visual appeal, offering a partially finished edge that improves appearance without the full expense of a closed pattern. Suitable for applications needing a moderate level of refinement.
The open end pattern is the standard option, where the perforated area begins and ends with partial or irregular rows due to the stepped perforating process. This approach is efficient and economical, ideal for non-decorative applications or areas that will be framed. However, it may lack the finished look needed for visible applications.
Closed end pattern
Semi closed end pattern
Open end pattern
Materials
Hexagonal perforation is available in a wide range of materials, including:
- Mild steel
- Stainless steel
- Galvanised steel
- Aluminium
- Brass
- Other alloys
